Tehaleh Summer Luau
Saturday, July 5, 2025 | 11:30 a.m. - 3:00 p.m.
Aloha!
Get ready to experience a luau-style celebration that honors the rich traditions of Hawai'i while embracing the diverse cultures of Polynesia — made up of many island nations and cultures.
We're working with local catering company Cafe Pacific Catering to bring in Hawaiian cuisine to bring the islands to you. Once we secure the menu, we will provide the menu and pricing involved for a Hawaiian plate lunch.
As you enjoy the delicious food, a live Hawaiian music band will set the mood with soothing island tunes throughout the event, creating the perfect tropical atmosphere.
Be captivated by hula dancing performances showcasing the beauty and elegance of hula, as dancers tell stories through graceful movements, traditional attire, and the rhythmic sounds of traditional Hawaiian music. And don’t miss the thrilling fire knife dancing performance with Samoan drumming — a breathtaking display of skill and flames that will light up your day!
Join us for an day full of island vibes, food, music, and unforgettable performances. Aloha and see you at the Summer Luau!
If you miss the RSVP deadline, please still come to the event as the RSVP is used to provide our vendors and staff an estimated attendance.
Get ready to experience a luau-style celebration that honors the rich traditions of Hawai'i while embracing the diverse cultures of Polynesia — made up of many island nations and cultures.
We're working with local catering company Cafe Pacific Catering to bring in Hawaiian cuisine to bring the islands to you. Once we secure the menu, we will provide the menu and pricing involved for a Hawaiian plate lunch.
As you enjoy the delicious food, a live Hawaiian music band will set the mood with soothing island tunes throughout the event, creating the perfect tropical atmosphere.
Be captivated by hula dancing performances showcasing the beauty and elegance of hula, as dancers tell stories through graceful movements, traditional attire, and the rhythmic sounds of traditional Hawaiian music. And don’t miss the thrilling fire knife dancing performance with Samoan drumming — a breathtaking display of skill and flames that will light up your day!
Join us for an day full of island vibes, food, music, and unforgettable performances. Aloha and see you at the Summer Luau!
If you miss the RSVP deadline, please still come to the event as the RSVP is used to provide our vendors and staff an estimated attendance.
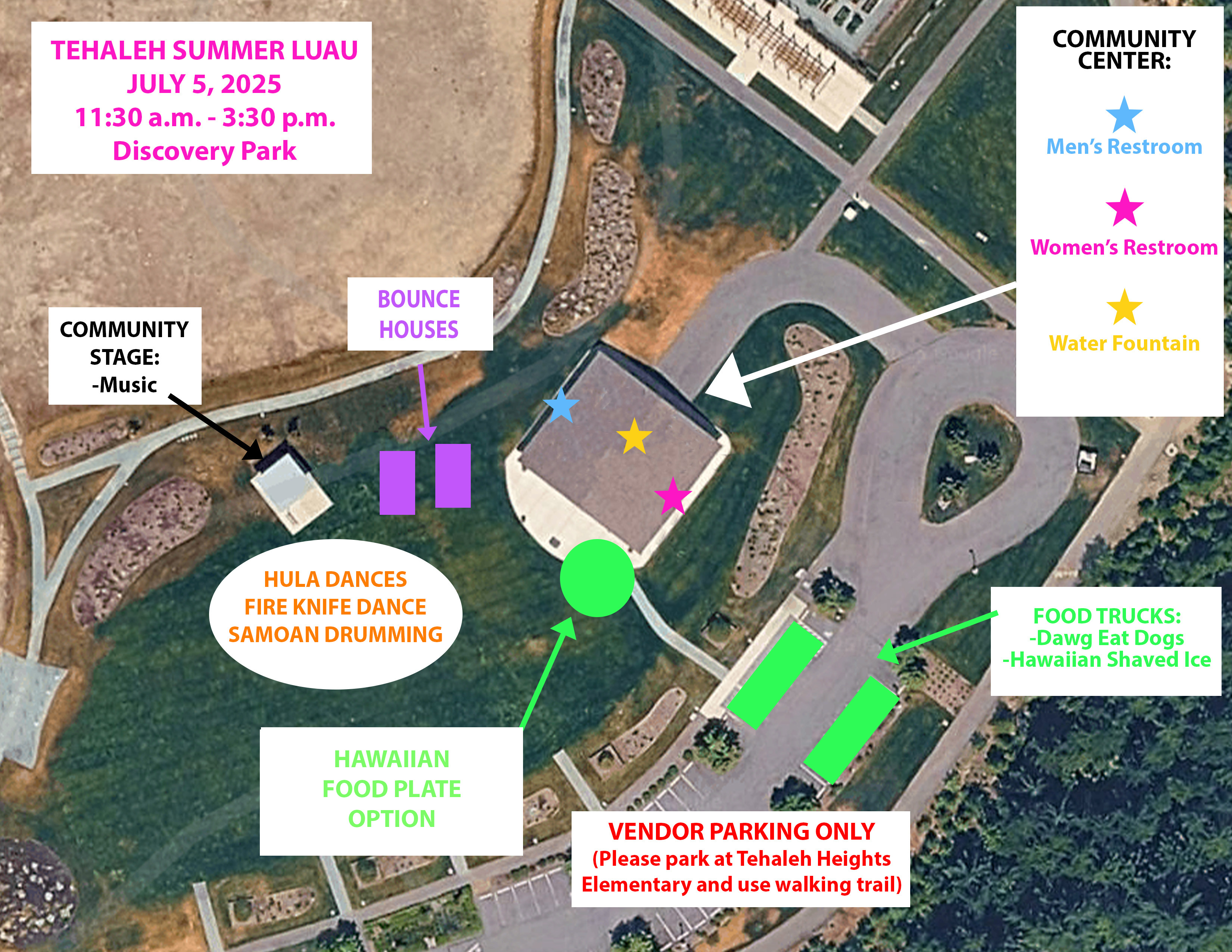
Location
Discovery Park
17834 Cascadia Boulevard East, Bonney Lake, WA 98391
17834 Cascadia Boulevard East, Bonney Lake, WA 98391
Date & Time
July 5, 2025
11:30 a.m. - 3:00 p.m.
11:30 a.m. - 3:00 p.m.






Schedule of the Day:
entire event
Live Music
Enjoy the sounds of the islands with a live band playing authentic Hawaiian music throughout the event! From start to finish, the band will set the perfect tropical atmosphere, with lively tunes that will keep you swaying along. They'll take a few breaks during the dance performances, but the music will keep flowing, adding a melodic backdrop to your luau experience!
entire event
Event Activities
While you enjoy the soothing island tunes and watch the performances, partake in various activities and food selections during the entire event:
-Palm tree bouncer
-Leaps 'n' bounds lava flow bouncer
-Ono Shaved Ice
-Dawg Eat Dogs
-Hawaiian-Themed Food Plate catered by Cafe Pacific Catering
-Palm tree bouncer
-Leaps 'n' bounds lava flow bouncer
-Ono Shaved Ice
-Dawg Eat Dogs
-Hawaiian-Themed Food Plate catered by Cafe Pacific Catering
12-12:30 PM
Hula Dancing
Get ready to groove to the rhythm of the islands with Hālau Hula Ka Lei Mokihana I Ka Ua Noe! Join us for an unforgettable luau experience with vibrant, energetic hula dancing. Be captivated by hula dancing performances that blend storytelling, graceful movement, and the vibrant beauty of traditional Hawaiian attire—all set to the soothing melodies of island music.
1-1:30 PM
Fire Knife Dancing & Samoan Drumming
Tupu Le Afi will be showcasing their mastery of fire knife dancing and traditional Samoan drumming, offering a captivating and culturally rich performance that honors their heritage and inspires future generations. The troupe aims to connect with Fa’aaloalo (respect), Mamalu (honor), and Aiga (family), ensuring the legacy of this ancient tradition endures. Join us for an unforgettable experience that celebrates the vibrant spirit of Polynesian culture.
2-2:30 PM
Hula Dancing
Get ready to groove to the rhythm of the islands with Hālau Hula Ka Lei Mokihana I Ka Ua Noe! Join us for an unforgettable luau experience with vibrant, energetic hula dancing. Be captivated by hula dancing performances that blend storytelling, graceful movement, and the vibrant beauty of traditional Hawaiian attire—all set to the soothing melodies of island music.
KNOW BEFORE YOU GO
PARKING
Parking at Discovery Park will be reserved only for vendors — remaining spots can be utilized by those with disabled/handicap placards.
Please park at Tehaleh Heights Elementary School and use the path pictured to walk around the pond to the community center area.
Please park at Tehaleh Heights Elementary School and use the path pictured to walk around the pond to the community center area.
PAYMENT
Food vendors at the event will be accepting both cash and card payments for your convenience.
However, we highly recommend bringing both forms of payment with you in case of any technical issues that may occur.
However, we highly recommend bringing both forms of payment with you in case of any technical issues that may occur.
FACILITIES
The Discovery Park Community Center will remain open throughout the duration of the event.
Guests are welcome to use the indoor facilities, which include restrooms and a convenient water bottle filling station.
We will also have tables set up to relax and eat in our air conditioned grand room.
Guests are welcome to use the indoor facilities, which include restrooms and a convenient water bottle filling station.
We will also have tables set up to relax and eat in our air conditioned grand room.
FOOD AND BEVERAGES
Try out this delicious hot dog cart, serving up gourmet dogs with a side of local flair.
From the iconic Seattle Dog topped with cream cheese and grilled onions to a classic American dog, their menu is a tasty journey for your taste buds.
From the iconic Seattle Dog topped with cream cheese and grilled onions to a classic American dog, their menu is a tasty journey for your taste buds.
https://www.facebook.com/onoiceshack/
Cool off with a taste of the islands!
A Hawaiian shaved ice truck will be serving up colorful, refreshing treats in a variety of tropical flavors—perfect for a summer afternoon at the Luau.
Cool off with a taste of the islands!
A Hawaiian shaved ice truck will be serving up colorful, refreshing treats in a variety of tropical flavors—perfect for a summer afternoon at the Luau.
HAWAIIAN PLATE
Enjoy mouthwatering Hawaiian food catered by Cafe Pacific Catering. Limited plate options, first-come, first-serve.
$15 plate: Huli Huli Chicken/Shredded Kalua Pork, fresh Hawaiian Rolls, Pineapple Slaw/Macaroni Salad, and a bottled water
$15 plate: Huli Huli Chicken/Shredded Kalua Pork, fresh Hawaiian Rolls, Pineapple Slaw/Macaroni Salad, and a bottled water
LEARN ABOUT POLYNESIA
What is Polynesia?
Polynesia is a large region in the Pacific Ocean made up of many island nations and cultures, including Hawaiʻi, Samoa, Tahiti, Tonga, and New Zealand (Aotearoa).
These cultures share deep connections through ocean navigation, storytelling, language, and respect for the land (ʻāina) and sea (kai).
These cultures share deep connections through ocean navigation, storytelling, language, and respect for the land (ʻāina) and sea (kai).
Polynesian dances
While hula is Hawaiian, it is part of the broader Polynesian cultural family, in the sense that many Polynesian cultures have traditional dances with spiritual or storytelling purposes.
Examples:
Siva (Samoa)
Tāmūrē (Tahiti)
Lakalaka (Tonga)
Haka (Māori, New Zealand)
Examples:
Siva (Samoa)
Tāmūrē (Tahiti)
Lakalaka (Tonga)
Haka (Māori, New Zealand)
Key Characteristics

-Common linguistic roots in the Austronesian language family
-Deep oral storytelling traditions
-Strong sense of genealogy, family, and community
-Rich music, dance, an tattooing traditions
-Close connection to land and sea
Polynesian Voyaging
Long before GPS, Polynesian navigators explored thousands of miles of ocean using only the stars, waves, and winds.
They traveled in double-hulled canoes (wa'a) and passed down knowledge through generations — an incredible example of science, skill, and tradition.
They traveled in double-hulled canoes (wa'a) and passed down knowledge through generations — an incredible example of science, skill, and tradition.
Polynesian Garlands
Leis are deeply embedded in Hawaiian culture, but many other Polynesian cultures have similar garlnds or adornments with distinct names and meanings:
Samoa - Ula (made from flowers or red pandanus seeds, worn during ceremonies
Tonga - Kahoa (a necklace of flowers or polished seeds, worn for decoration and status
Tahiti- Hei (flower crowns and garlands worn during dances, rituals, and festivals)
Samoa - Ula (made from flowers or red pandanus seeds, worn during ceremonies
Tonga - Kahoa (a necklace of flowers or polished seeds, worn for decoration and status
Tahiti- Hei (flower crowns and garlands worn during dances, rituals, and festivals)
Polynesian Language
Mālo/Talofa (Samoan) - Hello
Fa'afetai (Samoan) - Thank you
Mālo e lelei (Tongan) - Hello
Mālō (Tongan) -Thank you
la ora na (Tahitian) - Hello
Māuruuru (Tahitian) - Thank you
Kia ora (Māori) - Hello/Thank you
Ngā mihi (Māori) - Thank you
Pan-Polynesian refers to things that are shared across many or all Polynesian cultures:
Moana - Ocean
Mana - Spiritual energy/power
Fa'afetai (Samoan) - Thank you
Mālo e lelei (Tongan) - Hello
Mālō (Tongan) -Thank you
la ora na (Tahitian) - Hello
Māuruuru (Tahitian) - Thank you
Kia ora (Māori) - Hello/Thank you
Ngā mihi (Māori) - Thank you
Pan-Polynesian refers to things that are shared across many or all Polynesian cultures:
Moana - Ocean
Mana - Spiritual energy/power
Polynesian culinary
A "luau" is specifically a Hawaiian term, many of these foods reflect broader Polynesian culinary traditions:
-Taro/sweet potato
-Tropical fruits
-Kalua Pig (Hawai'i)
-Poi (Hawai'i)
-Lomi Lomi Salmon (Hawai'i)
-Laulau (Hawai'i)
-Haupia (Hawai'i)
-Oka/Ika Mata/Poke (Samoa/Tahiti/Hawai'i)
-Palusami (Samoa/Tonga)
-Fa'alifu Talo (Samoa)
-Taro/sweet potato
-Tropical fruits
-Kalua Pig (Hawai'i)
-Poi (Hawai'i)
-Lomi Lomi Salmon (Hawai'i)
-Laulau (Hawai'i)
-Haupia (Hawai'i)
-Oka/Ika Mata/Poke (Samoa/Tahiti/Hawai'i)
-Palusami (Samoa/Tonga)
-Fa'alifu Talo (Samoa)
"Modern" culinary
While these Hawaiian foods are still cultural, they are actually more modern!
Huli Huli Chicken (Hawaiian, modern)
Spam Musubi
(Hawaiian/Japanese fusion, popular in local cuisine)
Coconut Bread or Poi Rolls
Huli Huli Chicken (Hawaiian, modern)
Spam Musubi
(Hawaiian/Japanese fusion, popular in local cuisine)
Coconut Bread or Poi Rolls
LEARN ABOUT HAWAI'I
The meaning of Hula
Hula is more than just dance — it’s a way of telling stories, preserving history, and honoring Hawaiian gods, people, and nature.
Movements, chants (oli), and music all come together to share a message. Hula dancers wear traditional clothing and flowers to help express meaning—not just for decoration!
Movements, chants (oli), and music all come together to share a message. Hula dancers wear traditional clothing and flowers to help express meaning—not just for decoration!
Hawaiian Language
Aloha - Hello/Goodbye
Aloha - Love/Compassion
Mahalo - Thank you
Ohana - Family
Wahine - Woman
Kāne - Man
Keiki - Child or children
'Ono -Delicious
Pua - Flower
Mele - Song
Hula - Dance
Lani - Heaven or sky
Malama ʻāina: Care for the land
āina - Land
Kai - Sea
Aloha - Love/Compassion
Mahalo - Thank you
Ohana - Family
Wahine - Woman
Kāne - Man
Keiki - Child or children
'Ono -Delicious
Pua - Flower
Mele - Song
Hula - Dance
Lani - Heaven or sky
Malama ʻāina: Care for the land
āina - Land
Kai - Sea
What do flowers mean?
In Hawaiian culture, flowers represent love, connection, and natural beauty.
Left ear: You're taken
Right ear: You're single
Wearing a flower is a simple way to show aloha (love, compassion, and kindness).
Left ear: You're taken
Right ear: You're single
Wearing a flower is a simple way to show aloha (love, compassion, and kindness).
Art of Lei making
In Hawaiian culture, the lei is far more than a beautiful garland—it’s a gesture of love, welcome, and celebration.
Traditionally made from flowers, leaves, shells, or even feathers, each lei carries meaning depending on the materials and occasion.
Traditionally made from flowers, leaves, shells, or even feathers, each lei carries meaning depending on the materials and occasion.
HAWAIIAN LEGENDS
Pele
Pele is the powerful goddess of fire and volcanoes. According to legend, she travels across the islands creating land with her molten lava. Her temper is fierce, and her presence is said to still dwell in Kīlauea, one of Hawaiʻi’s most active volcanoes.
Māui
The demigod Māui noticed that the days were too short for people to work. Using a magical rope, he climbed to the top of Haleakalā and lassoed the sun, convincing it to slow its path across the sky—creating longer days for humanity.
Kamapuaʻa
Kamapuaʻa (the Pig-Man) is a shapeshifting demigod who can take the form of a wild boar. He’s known for his wild nature and for his complicated love-hate relationship with Pele. Their story symbolizes the balance between destruction (lava) and renewal (rain and growth).
Nāmakaokaha‘i
Nāmakaokaha‘i is Pele’s older sister and a powerful sea goddess. In some stories, the rivalry between them explains the tension between lava (land) and ocean—how new islands are born through their eternal conflict.
Join us on July 5
Photography and videography will be captured throughout the event, to be utilized by Tehaleh Community Life for purposes of promotion, websites, print, and social media. All participants agree to indemnify, defend, and hold harmless Tehaleh, its employees, volunteers, and affiliates from any claims, liabilities, damages, or expenses arising from participation in the the Tehaleh Summer Luau. This includes, but is not limited to, personal injury, property damage, or any other loss incurred before, during, or after the event. The participant(s) acknowledges and assumes all risks associated with the event and agrees to participate voluntarily.